How Is Software Architecture Boosting Digital Health?

The Latest Tech is Transforming the Healthcare Sector
The United States’ Food and Drug Administration (FDA), a leading federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services in the U.S., has stressed that “Artificial Intelligence and machine learning technologies have the potential to transform health care by deriving new and important insights from the vast amount of data generated during the delivery of health care every day.”
Thanks to all of the new possibilities that software architecture brings to this field, mid and senior-level software architects are now the true bearers of an industry-wide revolution for the healthcare sector. Here, we’ll explore diverse, industry-wide practical implementations of digital health around the world along with Snowflake’s latest digital health offering. Further, and perhaps most importantly, we’ll spotlight the global tech talent that’s leading in this field.

But First, What’s Digital Health?
The Digital Health & Care Innovation Centre (DHI), part of the Scottish Funding Council’s Innovation Centre Programme, defines digital health as an umbrella term to refer to big data, cloud computing, connected health, eHealth, gamification, health 2.0, health information technology, mobile health (mHealth), quantified self, precision and personalized medicine, telehealth, telemedicine, and wireless health. The center also identifies essential elements in digital health applications, which include “wireless devices, hardware and software sensors, microprocessors and integrated circuits, the internet, social networking mobile and body area networks, health IT, genomics and personal genetic information.”
In digital health, we basically categorize the latest tech tools under healthcare services or related processes and products. Those instruments include the Internet of Things, advanced computing, and big data analytics all the way to Artificial Intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and robotics.
Digital Health Benefits & Examples
The biggest improvement ML is bringing to healthcare is the power of data. Better able to conduct analytics, establish trends, and create algorithms, this technology is considerably optimizing the sector’s day-to-day insight for enhanced healthcare.
For example, when included as part of imaging systems, ML may offer improved skin cancer diagnostic information. In smart sensor devices, it may increase the capabilities of estimating the wearer’s odds of having a heart attack.
In other examples using AI-based algorithms, Computer-Aided Detection (CADe) systems and Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CADx) software at the service of radiological images, can assist with clinical diagnoses. And computer-aided triage (CADt) software can prioritize time-sensitive results.
This latest tech is essentially capable of putting patients requiring expedited medical attention at the top of an urgent list. At Newfire Global Partners, over 80% of our currently ongoing projects relate to digital health and we’re proud to be expanding current knowledge in this field.
The Complexity of Software Architecture in Digital Health
As logical as digital health may sound, software architecture for digital health doesn’t come as easily. On the contrary, every iteration in this field is part of highly challenging, yet also very impactful projects. To begin, consider the need for the highest safety, security, and health standards tied to working with big daily volumes of sensitive personal data and personally identifiable information. The health and safety of individual patients are at stake with every project.
In accordance with the World Health Organization (WHO), “Digital health should be an integral part of health priorities and benefit people in a way that is ethical, safe, secure, reliable, equitable and sustainable.” Moreover, efforts on this front “should be developed with principles of transparency, accessibility, scalability, replicability, interoperability, privacy, security, and confidentiality.” Big strides are needed in this field, which prioritizes immediate acceleration for development in the sector.
Amidst these necessities, we must also consider how digital health investors need the highest return rate possible with minimal risk, putting an added strain on the precise tools being supported. Tie this to user acceptance levels, and great questions are being raised around the exact digital health products and services that can effectively be used, as well as any corresponding gaps and opportunities in the field. Additionally, side effects and complications must be factored into the equation.
Software architects are therefore having to come up with solutions that aren’t only tied to prevention and detection, they also must respond to the everyday necessities and applications in the medical field with many stakeholders in mind. The ultimate challenge is to create efficient and sustainable systems that provide quality care that’s regulation-friendly, accessible to all and supports management, rehabilitation, and even palliative care.
As part of digital health global efforts, the WHO is actively calling stakeholders on the imminent need for advancement in digital health today. For them, the “application to improve the health of populations remains largely untapped, and there is immense scope for the use of digital health solutions.” As of July 2022, WHO is engaging in collaborative work for “inclusive, impactful, and responsible international research in AI and digital health” around the world. They’re also acting out on a five-year global strategy on digital health for the period of 2020-2025.
Seizing the Power of Data for Public Health
The COVID-19 pandemic is a perfect example of the need for acceleration in these efforts. This global health emergency indeed expedited digitalization. Examples include the WHO’s Facebook messenger chatbot to combat COVID-19-related misinformation as well as a dashboard to assist with data visualization of the pandemic. They also leveraged ML to deliver real-time numbers and situation reports, including symptom information shares, prevention initiatives, and other pertinent data. The application allowed contact in twenty languages to billions of people across the globe via WhatsApp. Altogether, this allowed WHO to work on the goal of promptly “keep[ing] people safe from coronavirus” when it mattered most.
WHO is currently focused on harnessing the “digital revolution towards urgent health challenges,” as well as “emphasizing equity and greater participation from low and middle-income countries (LMIC) in the research and development and governance of the digital health and AI space, with particular focus on the inclusion of young researchers and entrepreneurs.”
This is where mid and level senior software architects fit into this global picture.
Why Every Software Architect Should Want to Work in Digital Health

Being part of the digital health industry means working in an ever-changing, challenging, and demanding sector.
From an app that creates, collects, or simply shares patient data to smart devices that optimize what we know and can monitor vitals like blood pressure, blood sugar, medication compliance, and physical activity, there are also wider practical or medical uses to consider in this digital health revolution.
This year, Snowflake announced a new Healthcare and Life Sciences Data Cloud, which according to TechTarget, “provides optimizations for data types and formats commonly used in healthcare and life sciences, including unstructured data.” This availability is actively helping companies to scale…quickly!
In TechTarget’s opinion, per their interview with Snowflake’s healthcare and life sciences industry principal, Todd Crosslin, “the new service is contextually similar to the Financial Data Cloud that his company launched in 2021.” The implications of this comparison are obvious.
Snowflake has been one of the most disruptive tools in the financial sector for at least a year. Entities such as the New York Stock Exchange and Capital One jumped last September to become some of the first clients of Snowflake’s Financial Data Cloud release. Back then, the company had already presented this tool as a means “to launch customer-centric products and services, build fintech platforms of the future, and accelerate their compliance and regulatory compliance.” And they weren’t kidding. The disruption Snowflake has fostered in the financial sector has truly been game-changing.
Snowflake’s new opportunity now allows mid and senior software architects to be at the forefront of the latest healthcare advancement.
The Goals of the Digital Health Space
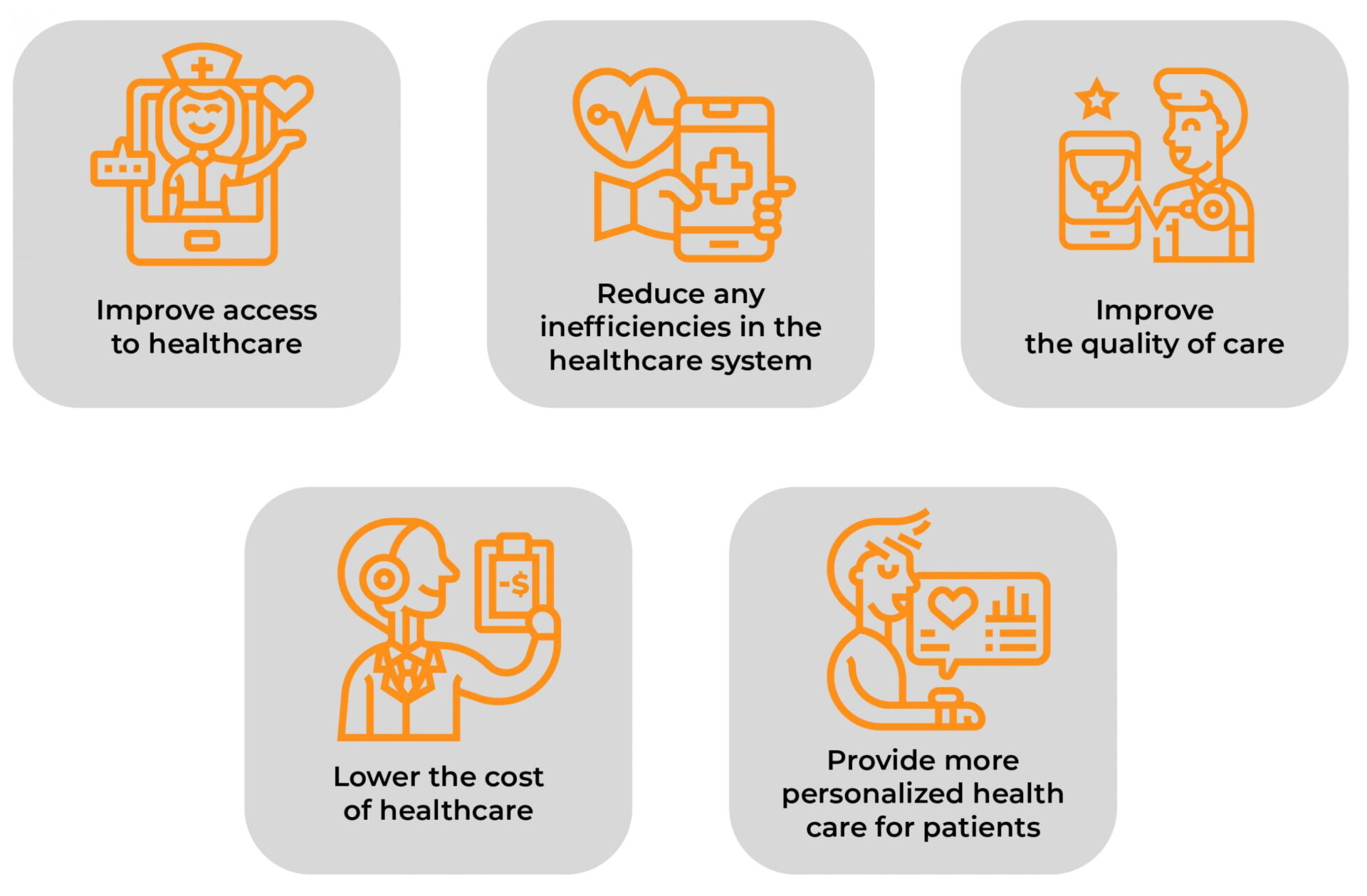
Anyone moving over to the digital health sector can expect to focus on the long list of functions and goals that StatPearls, a leading healthcare educational publishing house, presented at the National Library of Medicine for the National Center of Biotechnological Information. The punch list includes improving the quality of outcomes of care and service with a continued enhancement to population health, physician, non-physician, and patient experience as well as addressing health disparities overall.
In their words, Digital Health has been gaining momentum because it is envisioned to:
Why Partnering with a Leading Tech Company Can Make a Big Difference
The private sector is, of course, weighing in on the digital health revolution. Per Precedence Research, “the global digital health market was valued at $270.60B USD in 2021 and is expected to reach over $1354.68B USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR 19.2% during the forecast period 2022 to 2030.” Software architects can find a powerful ally in this sector to make a big dent in the digital evolution of healthcare.
New developments are certainly creating lucrative opportunities in this market. Amazon made its Care telehealth service available nationwide at the start of this year. This was a previous pilot program that’s now open to the entire U.S. And while IBM sold its Watson Health data and analytics business to a global investment company earlier this year, Oracle closed a $28.3B acquisition of Cerner, an electronic health record company, less than 6 months later in June 2022.
From online symptom checkers to patient portals, the world is now ready for cloud computing, big data, eHealth, and gamification, amongst other components of digital health, to take us into the new future of enhanced patient and health care. At Newfire Global Partners, we’re doing just that.
How about you? Where will you stand amidst this coming revolution? Lead a digital health innovation of the highest quality! We invite you to further your career with Newfire and take your growth to the next level.
